Understanding Root Cause Analysis
Definition and Importance
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) involves identifying the underlying reasons for problems, rather than merely addressing the symptoms. In the context of medical and IVD devices, RCA helps to understand why a failure occurred, which enables the implementation of effective corrective and preventive actions (CAPA).
Applications in Medical and IVD Devices:
- Quality Control: Ensures devices meet safety and performance standards, reducing the risk of defects.
- Regulatory Compliance: Satisfies the requirements of regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EU MDR.
- Patient Safety: Prevents adverse events, ensuring devices function as intended and are safe for use.
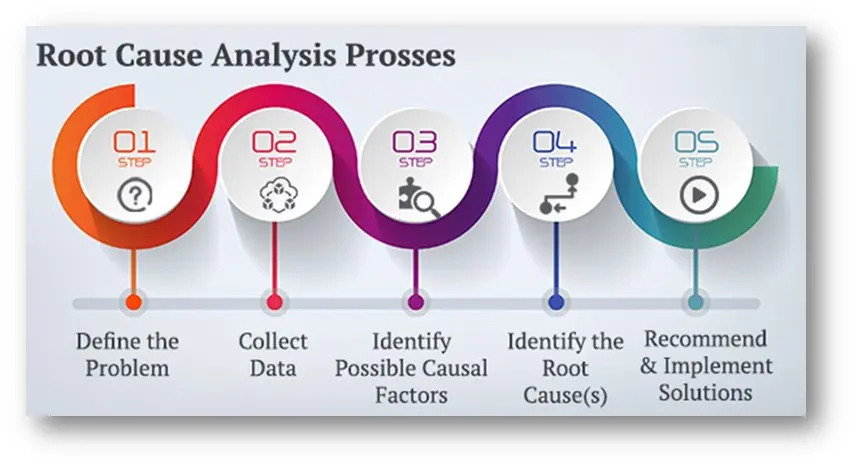
The Root Cause Analysis Process
Step-by-Step Approach
Problem Identification: Clearly define the problem, including details on when and where it occurred. This step sets the foundation for the entire RCA process.
Data Collection: Gather comprehensive information related to the problem. This includes production records, inspection reports, customer complaints, and any other relevant data. Accurate data collection is crucial for understanding the context and specifics of the issue.
Causal Factor Charting: Create a detailed timeline of events leading up to the problem. This helps in visualizing the sequence of occurrences and identifying potential causal factors. Tools like flowcharts and timelines can be used for this purpose.
Root Cause Identification:
Utilize specific techniques to determine the root cause of the problem. Common methods include:- 5 Whys: Involves repeatedly asking "Why?" until the fundamental cause is identified.
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa): Categorizes potential causes into groups such as people, process, materials, and equipment, helping to organize and visualize the contributing factors.
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): A top-down approach that uses Boolean logic to identify potential causes of a system failure.
Corrective Action Implementation:
Develop and implement actions to address the identified root cause. This may involve changes in processes, materials, or training to prevent recurrence. The corrective actions should be specific, actionable, and targeted at the root cause.Verification and Validation: Ensure that the corrective actions are effective in preventing recurrence of the problem. This involves testing and monitoring the changes to confirm that the issue has been resolved and does not reoccur.
Documentation and Reporting:
Maintain detailed records of the RCA process and its outcomes. Proper documentation is essential for regulatory compliance and for providing a reference for future RCA activities. Reports should include all steps of the RCA, from problem identification to verification and validation of corrective actions.