Medical Device Stability Testing is conducted to determine the environmental effects such as temperature, light, moisture, pH, agitation, gravity on product strength, quality, and purity. Such testing’s are conducted in the life sciences, chemical, medical devices, IVDs, pharmaceuticals, and food industries. Stability testing provide evidence to establish product storage and expiry dating criteria.
The medical devices stability testing determines the extent to which a device holds-on, within specified limits, and throughout its period of storage and use, the same properties, and characteristics that it possessed at its time of manufacture. Similar to pharmaceutical products, medical devices have a set of criteria to evaluate stability such as:
- Chemical – Degradation, Interaction, Device packaging and interaction, Radioactive decay, Manufacturing
- Physical – Physical characteristics, Manufacturing process, Storage conditions
- Microbiological – Sterility, Environmental control, Antimicrobial effectiveness
- Therapeutic
- Toxicological
- Biocompatibility
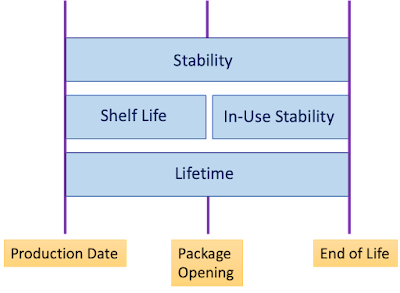
Applicability of Shelf Life Claim
With reference to the rules and regulation for medical devices and IVDs the Claim of
Shelf life is not applicable only if
Provided Further that, if the device is supplied sterile then the Stability Study is conducted to claim the effectiveness of sterility,
Determining the Medical Device Stability Testing
While determining the stability of medical devices following are also considered:
- Storage conditions, e.g., temperature variations, relative humidity, ventilation, air pressure, air-borne contamination, visible light, and other radiation, etc.
- The type of the device and intended use.
- The components or materials used for the manufacturing of the device.
- Method of manufacture
- Packaging, e.g. Products that are packaged in different sizes of packages may each have different stability or shelf life due to the difference in packaging area coming in contact with the product. Transportation conditions, e.g., vibration, shock, temperature, humidity, pH, etc.
Objectives of Stability Testing and Corresponding Study Types
| Objective |
Type of Study |
Use |
| To select adequate material of construction and container closure systems from the viewpoint of stability |
Accelerated |
Development of the product |
| To determine shelf-life and storage conditions |
Accelerated and real-time |
Development of the product and of the registration dossier |
| To substantiate the claimed shelf-life |
Real-time |
Registration dossier |
| To verify that no changes have been introduced in the material of construction or manufacturing process that can adversely affect the stability of the product |
Accelerated and real-time |
Quality assurance in general, including quality control |
Intended Market
The design of the stability testing programm should take into account the intended market and the climatic conditions in the area in which the medical device will be used. Four climatic zones can be distinguished for the purpose of worldwide stability testing, as follows:
- Zone I: temperate.
- Zone II: subtropical, with possible high humidity.
- Zone III: hot/dry.
- Zone IV: hot/humid.
Design of Stability Studies for Medical Devices and In-Vitro Diagnostic Devices
Stability studies for medical devices and in-vitro diagnostic devices (IVDs) should be tailored based on the inherent properties and stability attributes of the product, along with considering the climatic conditions prevalent in the target market area. Before commencing stability assessments for medical devices and IVDs, it is essential to gather, analyze, and review information regarding their stability characteristics.
Designing stability studies for medical devices and in-vitro diagnostic devices (IVDs) requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure accurate and reliable results. Here are some key points to consider when designing stability studies for medical devices and IVDs:
- Objective of the Study: Clearly define the purpose of the stability study, whether it is to determine shelf-life, assess the effects of storage conditions, or verify the stability of the product over time.
- Selection of Test Parameters: Identify the critical parameters to be monitored during the stability study, such as temperature, humidity, light exposure, and mechanical stress. These parameters should be selected based on the device's intended use, materials, and expected storage conditions.
- Study Design: Determine the study design, including the duration of the study, frequency of testing, and number of samples to be included. Consider whether accelerated aging studies, real-time studies, or a combination of both are appropriate for evaluating stability.
- Sample Preparation: Define the method for preparing test samples, including packaging, labeling, and storage conditions. Ensure that samples are representative of the final product and are stored in appropriate containers to maintain their integrity.
- Testing Methods: Select appropriate testing methods to evaluate the stability of the device, such as visual inspection, functional testing, and chemical analysis. Ensure that the chosen methods are validated and capable of detecting changes in the device's performance or properties.
- Documentation: Prepare the necessary documents for the stability study, including a study protocol outlining the study objectives, methods, and acceptance criteria. Maintain detailed records of all study activities, including sample handling, testing procedures, and results. All the level of documentation shall be in accordance with Quality Management System of the organisation.
- Regulatory Requirements: Identify the regulatory requirements governing stability studies for medical devices and IVDs in target markets. Ensure compliance with relevant standards and guidelines, such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility and ISO 13485 for quality management systems.
- Data Analysis: Establish criteria for evaluating stability data and determining the shelf-life of the device. Use statistical methods to analyze the data and make informed decisions about the device's stability under different conditions.
Climatic Zones for Stability Studies
The climate is different in all the countries in the world. For stability studies, climatic zones are categorized based on environmental conditions that may impact the performance and integrity of medical devices and in-vitro diagnostic devices (IVDs). These zones help determine appropriate storage conditions and testing parameters to assess the stability of the products.
| ICH Stability Zones |
Type of Climate |
| Zone I |
Temperate zone |
| Zone II |
Mediterranean/subtropical zone |
| Zone III |
Hot dry zone |
| Zone IVa |
Hot humid/tropical zone |
| Zone IVb |
Hot/higher humidity |
These stability studies zones are created due to the difference in temperature and humidity in different parts of the world. These zones have different ICH stability conditions for products. Following are ICH stability conditions for these zones.
Long Term Stability Testing Conditions
| Climatic Zone |
Temperature |
Humidity |
Minimum Duration |
| Zone I |
21ºC ± 2ºC |
45% RH ± 5% RH |
12 Months |
| Zone II |
25ºC ± 2ºC |
60% RH ± 5% RH |
12 Months |
| Zone III |
30ºC ± 2ºC |
35% RH ± 5% RH |
12 Months |
| Zone IVa |
30ºC ± 2ºC |
65% RH ± 5% RH |
12 Months |
| Zone IVb |
30ºC ± 2ºC |
75% RH ± 5% RH |
12 Months |
| Refrigerated |
5ºC ± 3ºC |
No Humidity |
12 Months |
| Frozen |
-15ºC ± 5ºC |
No Humidity |
12 Months |
Accelerated and Intermediate Stability Testing Conditions
| Climatic Zone |
Temperature |
Humidity |
Minimum Duration |
| Accelerated Ambient |
40ºC ± 2ºC |
75% RH ± 5% RH |
6 Months |
| Accelerated Refrigerated |
25ºC ± 2ºC |
60% RH ± 5% RH |
6 Months |
| Accelerated Frozen |
5ºC ± 3ºC |
No Humidity |
6 Months |
| Intermediate |
30ºC ± 2ºC |
65% RH ± 5% RH |
6 Months |
Factors Influencing Stability Studies of Medical Devices
Stability studies for medical devices and IVDs are influenced by various factors that must be carefully considered during the design and implementation of these studies. Here are some key factors:
- Device Characteristics: The design, materials, components, and intended use of medical devices and IVDs play a crucial role in their stability profiles. Factors such as exposure to environmental conditions, mechanical stress during use, and chemical interactions with bodily fluids or reagents may impact device stability over time.
- Environmental Conditions: Stability studies must account for the environmental conditions to which medical devices and IVDs are exposed during storage, transportation, and use. Variations in temperature, humidity, light exposure, and atmospheric pressure can affect device performance and integrity. It's essential to replicate real-world conditions as closely as possible in stability testing protocols.
- Packaging and Sterilization: The packaging materials and sterilization methods used for medical devices and IVDs can significantly influence their stability. Packaging must provide adequate protection against external factors such as moisture, light, and microbial contamination while maintaining product sterility and integrity. Similarly, sterilization processes should be validated to ensure they do not compromise device stability or functionality.
- Storage and Handling: Proper storage and handling practices are critical for maintaining the stability of medical devices and IVDs throughout their lifecycle. Instructions for storage conditions, shelf life, and handling procedures should be clearly defined and validated to minimize the risk of degradation or malfunction. Healthcare professionals and end-users must be educated on the importance of following these instructions to preserve device stability and ensure patient safety.